Carton glossary
Pre-press terms
DTP Desktop Publishing
Cutting order Implementation on the approved cardboard support of a unit cut on a plotter, faithfully reproducing the creasing and cutting rules of an industrial cutting die. The cutting order should comply with the client’s size instructions.
Repro Quality Print This stage will trigger the launch of tools (Offset slabs, Cyrel varnish, Printing plates, cutting die, etc.)
Bleed Printing area to be trimmed off which makes it possible to account for cutting tolerance, while ensuring that no unprinted edges occur.
Colour sample strip (Comes from dressmaking, fabric samples, etc.) Search in the laboratory for shades issued on the cardboard support chosen by the client. Development stage allowing the preparation of the Press Proof.
CTP Computer to Plate : Machine that “develops” aluminium slabs for offset machines by removing the former manufacturing stages of films and editing.
Press proof Official approval of the beginning of production (mostly in Offset for our business sector) in the client’s presence.
The “Printing” (Also called Run Proof) will have to comply with this substantiating document.
Paperboard terms
Delamination Paperboard layers (plys) separating from each other
Depression Impact / deformation of the paperboard layers without puncturing
GC1 Designates board made using mechanical pulp: interior wood / white back. Board also called “fully coated white back”. White coated front – inside wood – white back (see model no. 2)
GC2 Designates card made using mechanical pulp: interior wood / white back. Card also called “fully coated all wood”. White coated front – inside wood – white back (see model no. 3).
GD Designates paperboard made of recycled fibre.
GZ Designates paperboard made using bleached chemical pulp: Board also called “pure cellulose”. White coated front – inside wood – white back or coated (see model no. 1)
Grammage Weight per m2
Ply impurities Spots or particles of any colour can provide relief on the surface of the board.
Stiffness Stiffness of the board
Lamination terms
Lamination Process consisting of applying a film to the surface of a board using a laminator or lamination machine => metallic film or transparent film (gloss, matte, satin). This film is glued on with a water-based glue (or can be solvent-based glue).
Greyed Small grey points over the entire surface
Stringing (= no lamination = stria) Streaking of the laminate caused by impurities in the glue deposited on the gluing cylinder.
Lack of metallization Spot without metallic effect, the polyester layer of the laminate is present however
Orangeskin Lamination does not seem perfectly taut, small areas of the surface of the lamination look like the skin of an orange.
Marbled lamination Lamination that does not seem perfectly taut, small areas of different contrast that look like a marbled surface.
Printing terms
Offset Flat printing technique that uses a metal plate. The ink is transferred to the paper via a wet rubber cylinder called the Blanket. Offset is based on the mutual repulsion of ink and water. Only the oily (inked) parts print. Comes from the term “set off” (transfer).
Screenprinting Printing technique that uses screens between the ink and the medium with ink or varnish deposition superior to offset.
Fade A small surface on which the printing of a text, logo or graphic is partially absent
Blocked printing Refers to small regions of text, logos or graphics whose parts are normally “scooped out” and here are printed abnormally
Raised printing Refers to text, logos or graphics that are thicker than the underlying graphic.
Ghosting Text, logo or graphic printed a second time with the same colour but very faint intensity
Smudge: Generally caused by the back rubbing against the front leaving vertical traces of ink
Hickies Small faults generated during printing (lack of or too much ink)
Dry spots Small points of colour caused by water / ink imbalance during offset printing
Veiling Very faint intensity solid colour present on the entire surface caused by a water / ink imbalance during offset printing
Zone (=chimney) Surface (of random dimensions) with colour that contrasts with the rest
Gilding terms (= hot marking) or embossing
Gilding (=hot marking) Operation that consists of hot-transferring a hot or cold metal film onto a compatible substrate in the form of decoration or text using a marking tool (called a gilding iron).
Stamping Process that creates a sunken pattern on a material using a reverse-engraved block.
Embossing Process that creates a relief pattern using a relief-engraved block.
Lack A small surface on which the hot marking of a text, logo or graphic is partially absent
Raised hot marking Text, logos or graphics that are thicker than the underlying graphic.
Burning Small points of hot marking present on hot-marked graphics
Ragged hot marking Contours of hot-marked graphics that appear ragged under a magnifying glass
Hot raised marking Looks identical to hot embossing but the relief is created by a hot marking tool
Hot inlay marking Dust, streaks “imprisoned” in a hot marking; can be caused by a fault in a hot marking tool
Hot picket marking Small points of hot marking present on hot-marked graphics
Powdering Hot marked strips of dust
Cutting terms
Cutout Transformation operation during which a sheet of board is scored and cut out according to the contours of a drawing, using a flat or embossed form with fillets.
Angelhair Cutting faults
Stop Small scoring on the top tongue which is one of the elements allowing the closure of a container to stay shut
Mid-scored Trace of fold beside and roughly parallel to the score of the adhesive flaps
Attachment point Protuberance of the board on the rim of the container (essential for the container to be held on the frame during cutting)
Slot Space between the inside top or bottom rebate and the face (front or back) that allows the top tongue to be inserted
Scoring Deformation of the container material making it easier to fold when opening up the box
Exploded scoring The relief of the scoring of the back ply of the box is crazed (back of box)
Incomplete scoring Scoring that has not gone far enough
Interlocking Closure system that avoids opening the flap
Gluing terms
Gluing Transformation operation that consists of assembling a container using an adhesive
Shearing Checking the holding power of an adhesive by separating the two glued parts (glued flaps)
False ply Fault represented by a gluey fold beside the score
Icing Container that unglues easily despite the presence of adhesive with no shearing of the box
Perforation in the adhesive (=guillochet) Small perforations (cutouts) in the glue flap to help the gluing of the container
Glue point Drop of glue in a random position on the faces of the container that can prevent it opening out
Pool cue Streak of glue on the glue flap (visible when the container is assembled)
Other terms
Abrasion Traces of rubbing caused by movement of the container during truck transport
ECMA Code European Carton Makers Association
The ECMA operates three sizes of paperboard once opened out in the following order: A x B x H
Positioning Placement of a container on its imposition (represented by a number )
Register Refers to the perfect juxtaposition of techniques to give a perfect image of the superposition of embossing with printing or gilding => positioning fault
Triptych Colour range including the benchmark, as well as the minimum and maximum accepted
Tiling Refers to the curvature of the container due to imbalance between the humidity content of its components or too high tension in the lamination film => this phenomenon is generated over time
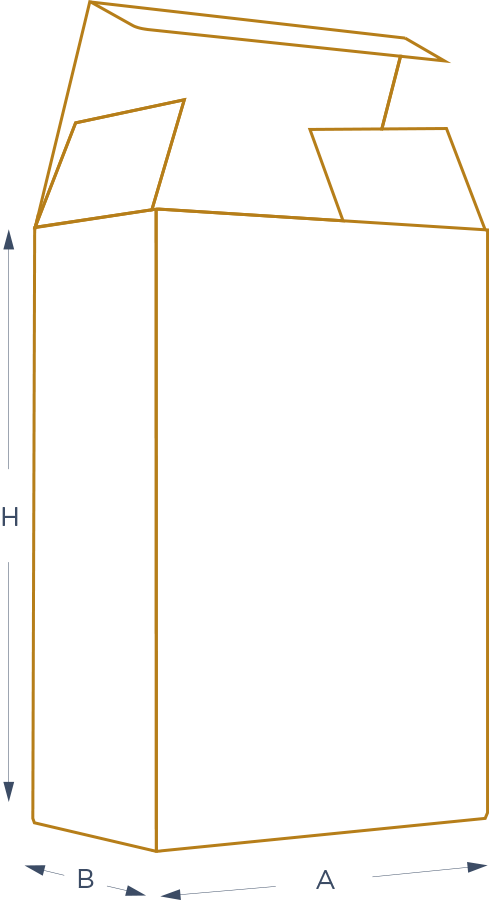

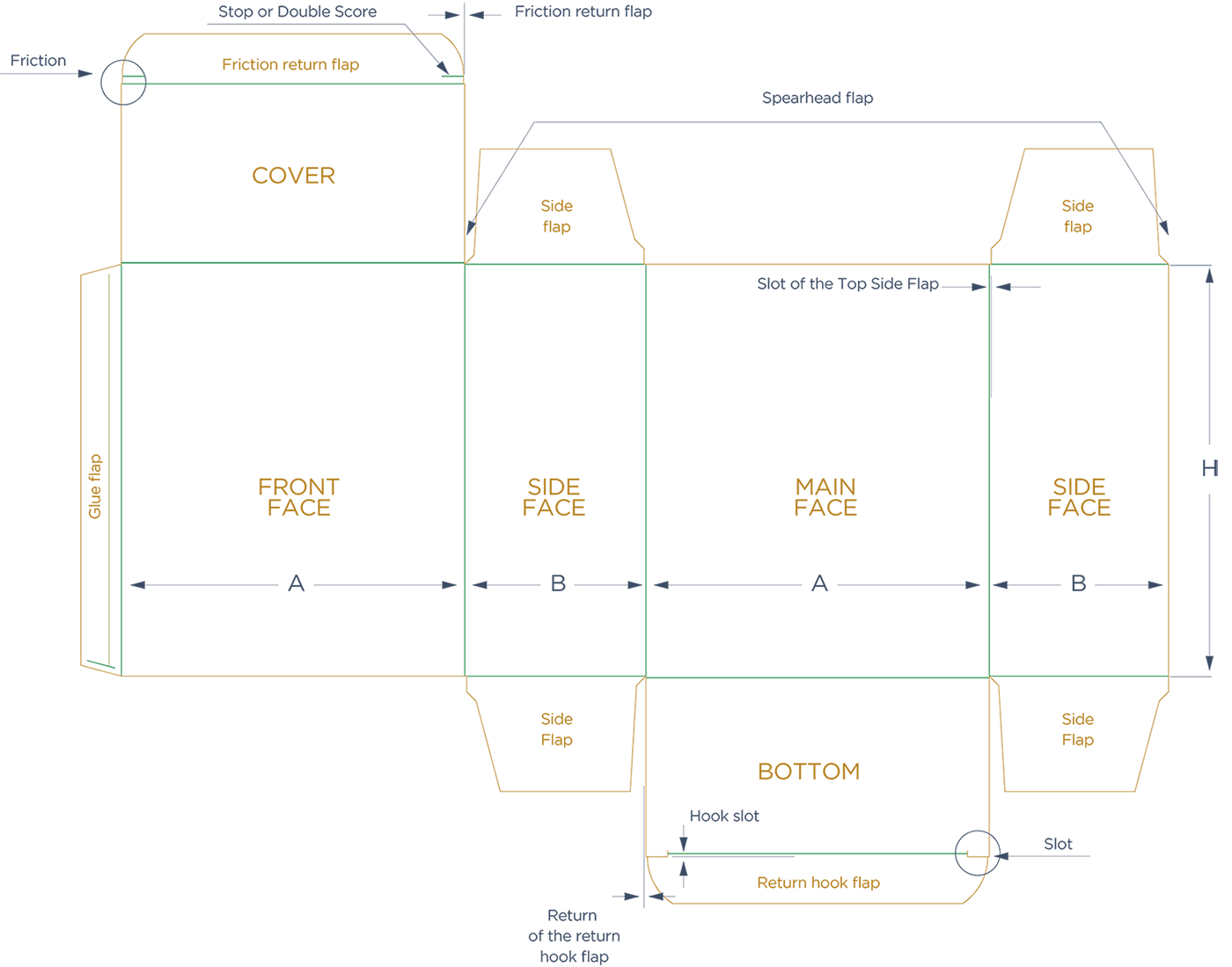
COMMON GLUED CARTONS
A = Parallel lid attachment direction
H = Along the gluing flap
B = The other one
Drawing and terms of a container